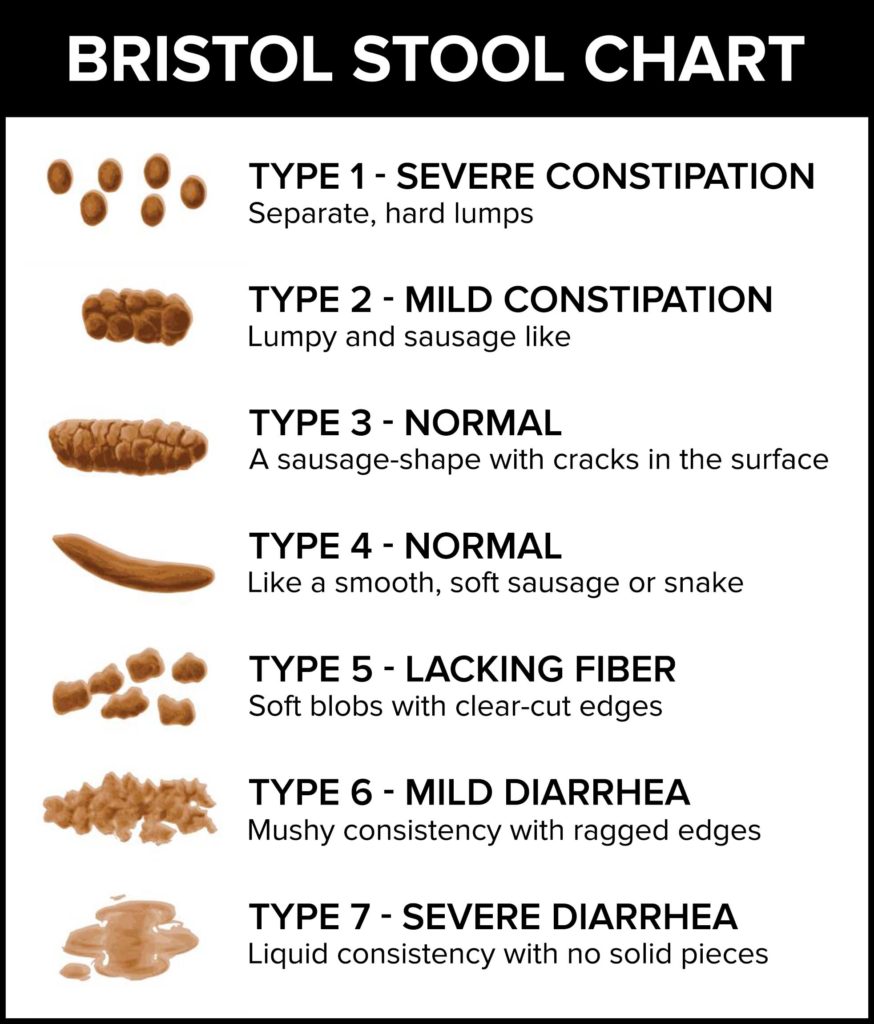
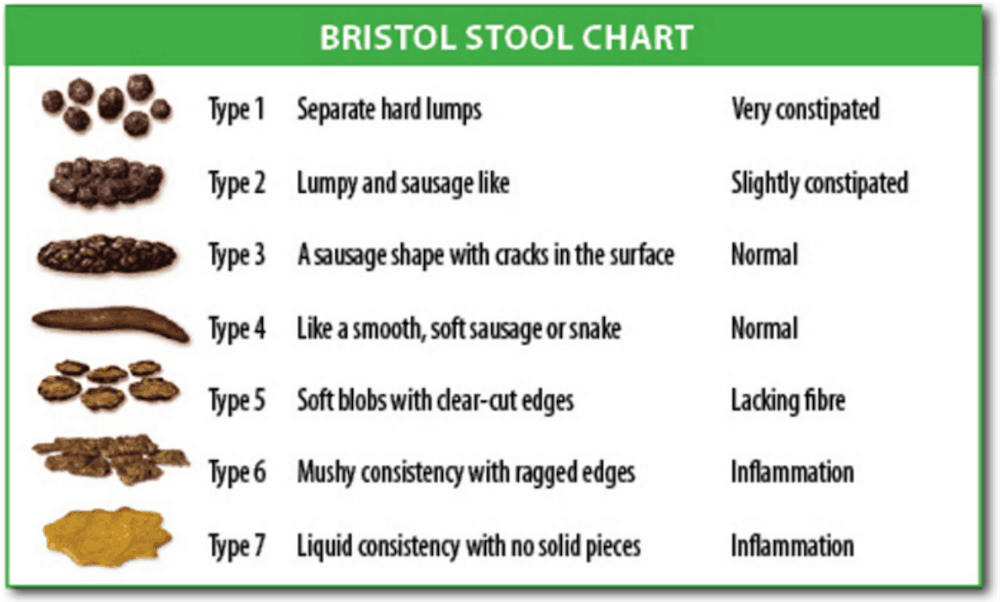
Oily Diarrhea That Floats

Greasy stool or steatorrhea means that you have too much fat in your stool.
Oily diarrhea that floats. Oily bowel movements or diarrhea are indicated by oil droplets which float in the toilet water stools that may have white or yellow fat in them or stools that float this is caused by a large amount oil in the stool. The medical term for this type of fatty stool is steatorrhea. Some people have even reported orange or waxy bowel movements. For example you may have oily stool after a fatty meal or it could.
It may also appear frothy gray to pale yellow. These include proteins fibers and salts. Most of the time a floating stool is the result of something you ate. The term fatty stool is used to describe stool that is greasy or oily often floats and is bulky.
Excessive gas in the stool. The two most common causes of floating stools are excess gas and malabsorption or poor absorption of nutrients. A floating stool also looks very fatty or greasy and the symptom persists for more than a few days a person experiences chronic constipation or diarrhea the stool is very light or pale. If you notice that your stool floats and appears greasy pale and abnormally foul smelling you should consult your doctor.
Steatorrhea or fatty stool occurs when there is too much fat in the stool. Foods that commonly cause gas contain. Certain medications such as large doses of bismuth subsalicylate kaopectate pepto bismol and other anti diarrheal drugs. If you eat something that causes gas or eat a large meal the gas mixes in with stool in the intestines.
Certain foods can cause gas in your stools. This is especially true if you have other symptoms of malabsorption. Usually stool with a higher amount of fatty substance has an oily look and it floats in the toilet. Stool or feces contain a mixture of undigested nutrients.
In mild cases steatorrhea may remain unnoticed for long periods of time. Depending on the reason why the stool is greasy it could happen occasionally. Excess fat in the stool such as due to a malabsorption disorder for example celiac disease. The extra air makes poop less dense causing it to float when it hits the toilet bowl.
Fatty stool often sticks to the sides of the toilet bowl and it is more difficult to flush away.